ESPAÑOL – INGLÉS
PALABRA Ó FRASE Nº333
‘INSOLACIÓN’ nombre SUNSTROKE.
‘INSOPORTABLE’ verbo UNBEARABLE.
‘INSPECCIÓN’ nombre INSPECTION.
Geografía e historia natural
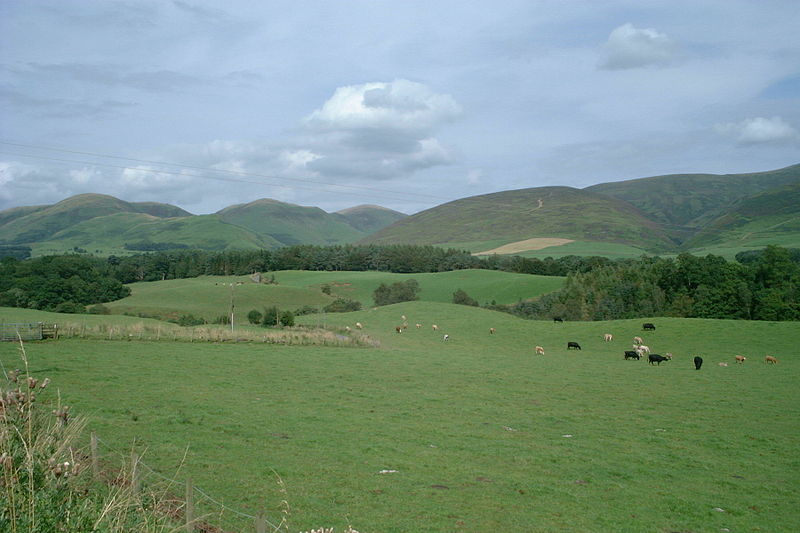
Escocia ocupa aproximadamente el tercio superior de la isla de Gran Bretaña, al noroeste del continente europeo. En total, su territorio abarca 78.772 km².33 La única frontera de Escocia en tierra firme es la que le une por el sur con Inglaterra, y que mide alrededor de 96 km, entre el río Tweed en la costa este y el fiordo de Solway en la oeste. El océano Atlántico rodea el norte y oeste de Escocia, mientras que al este se encuentra el mar del Norte. Irlanda se encuentra a sólo 30 km desde la península de Kintyre, mientras que Noruega queda a 400 km al noreste, las islas Feroe a 310 km e Islandia a 798 km al noroeste. El centro geográfico de Escocia, tradicionalmente, se sitúa a pocos kilómetros de Newtonmore, en Badenoch, al norte de las zonas más pobladas, aunque existen diversas opiniones al respecto, dependiendo del modo empleado para las mediciones, o de si se toman en consideración o no las islas escocesas.
La extensión territorial actual de Escocia es muy similar a la establecida en el Tratado de York de 1237 entre Inglaterra y Escocia34 y en el Tratado de Perth de 1266 entre Escocia y Noruega.35 Existen algunas excepciones: la Isla de Man, que antes era territorio escocés, es ahora una Dependencia de la Corona británica; las islas Órcadas y Shetland fueron adquiridas a Noruega en el siglo XV;33 mientras que Rockall, un pequeño islote rocoso en el Atlántico, fue anexionado al Reino Unido primero y a Escocia después por el Acta de la Isla de Rockall de 1972.36 37 Sin embargo, la legalidad de esta anexión ha sido puesta en tela de juicio por Irlanda, Dinamarca e Islandia, y probablemente no tiene efectos en el derecho internacional.38 39
=================================EN INGLÉS===============================
Geography and natural history
Main article:. Geography of Scotland
terrain map of Scotland stock
Scotland occupies approximately the upper third of the island of Great Britain, northwestern Europe. In total, its territory covers 78,772 km ² .33 The only Scottish border is on land that connects to the south with England, which is about 96 km, between the River Tweed on the east coast and the Solway Firth on the west. The Atlantic Ocean surrounds the north and west of Scotland, while the east is the North Sea. Ireland is just 30 km from the peninsula of Kintyre, while Norway is 400 km to the northeast, the Faroe Islands and Iceland to 310 km to 798 km to the northwest. The geographical center of Scotland, traditionally, is situated a few miles from Newtonmore in Badenoch, north of the more populated areas, although there are different opinions, depending on the mode used for the measurements, or if taken into consideration or not the Scottish islands.
Current territorial extent of Scotland is very similar to that established in the 1237 Treaty of York between England and Escocia34 and the 1266 Treaty of Perth between Scotland and Noruega.35 There are some exceptions: the Isle of Man, formerly Scottish territory, is now a dependency of the British Crown; Orkney and Shetland islands were acquired from Norway in the fifteenth century, 33 while Rockall, a small rocky island in the Atlantic, was annexed to the United Kingdom first and Scotland after the Act of the Island of Rockall in 1972.36 37 However, the legality of the annexation has been called into question by Ireland, Denmark and Iceland, and probably has no effect on the right internacional.38 39