Español – Inglés
PALABRA Ó FRASE Nº 1078
‘ESTRUJAR’ verbo
1 (limón) TO SQUEEZE.
2 (papel) TO CRUMPLE UP.
3 (trapo,ropa) TO WRING OUT [pt.& pp. wrung].
PUEBLOS GERMÁNICOS
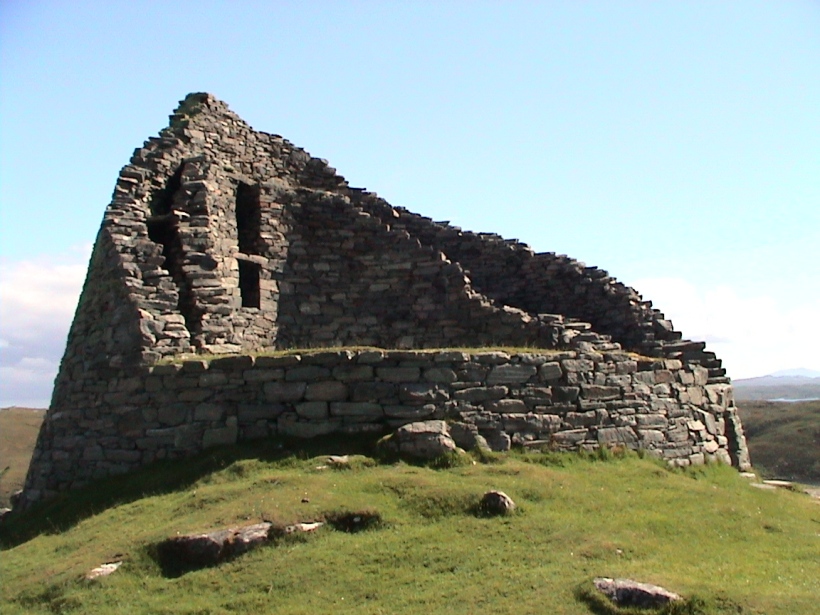
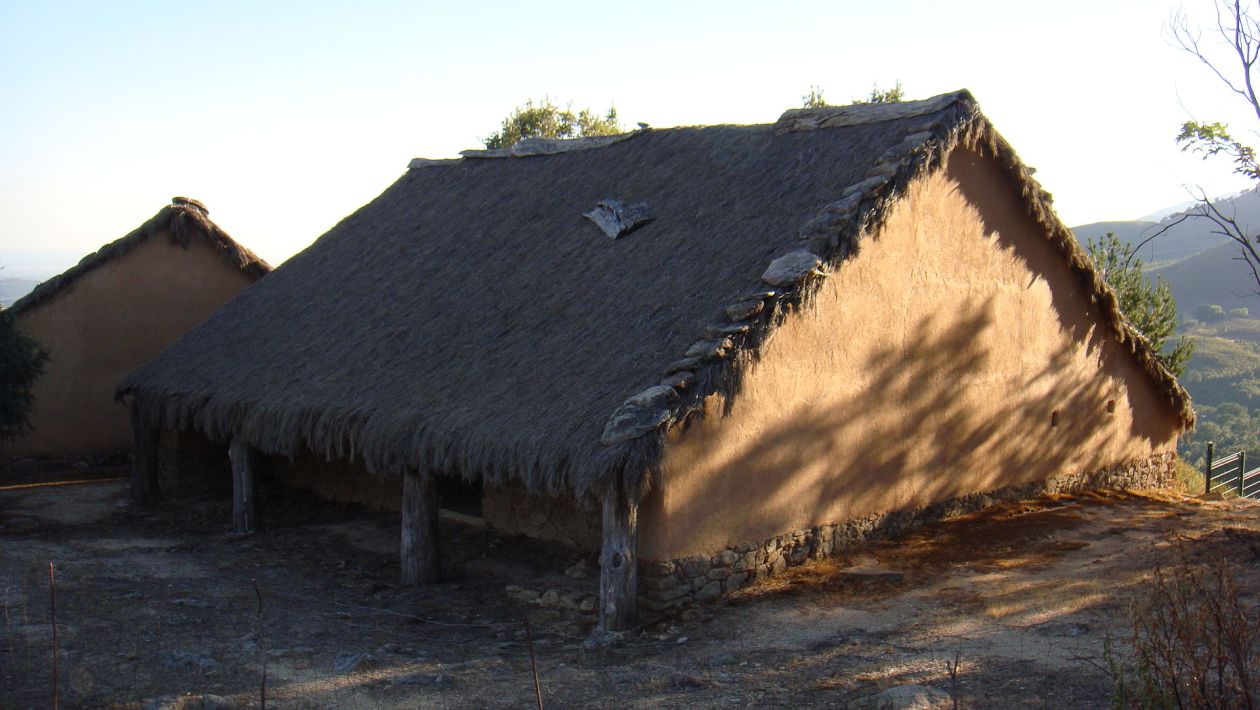
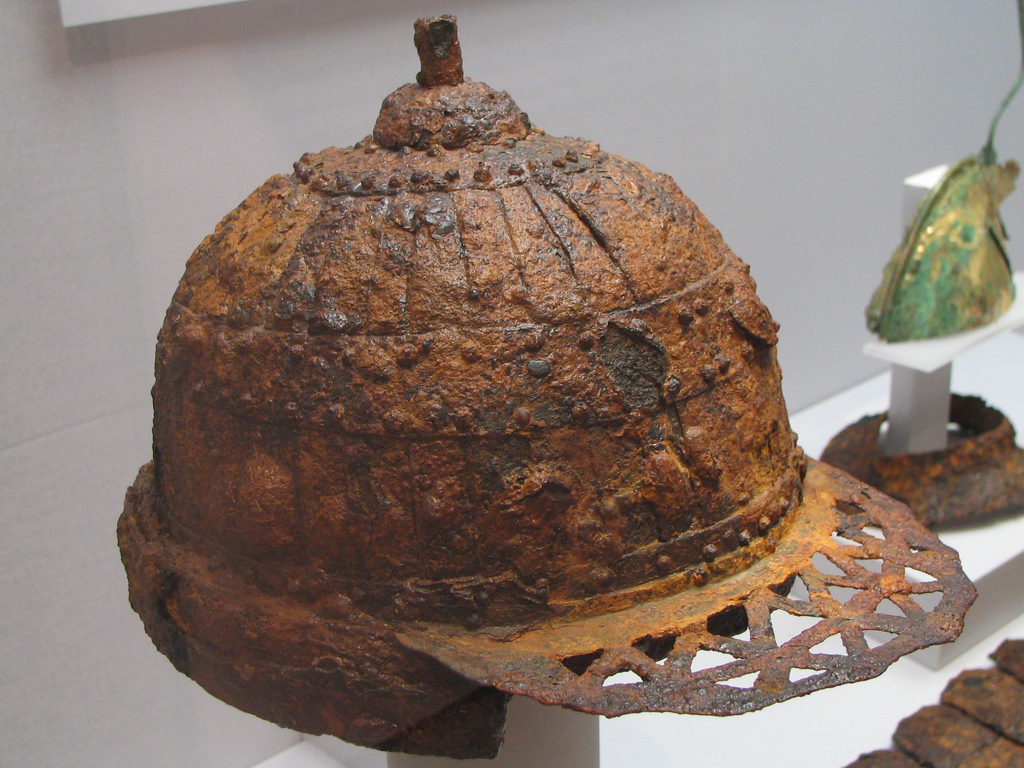
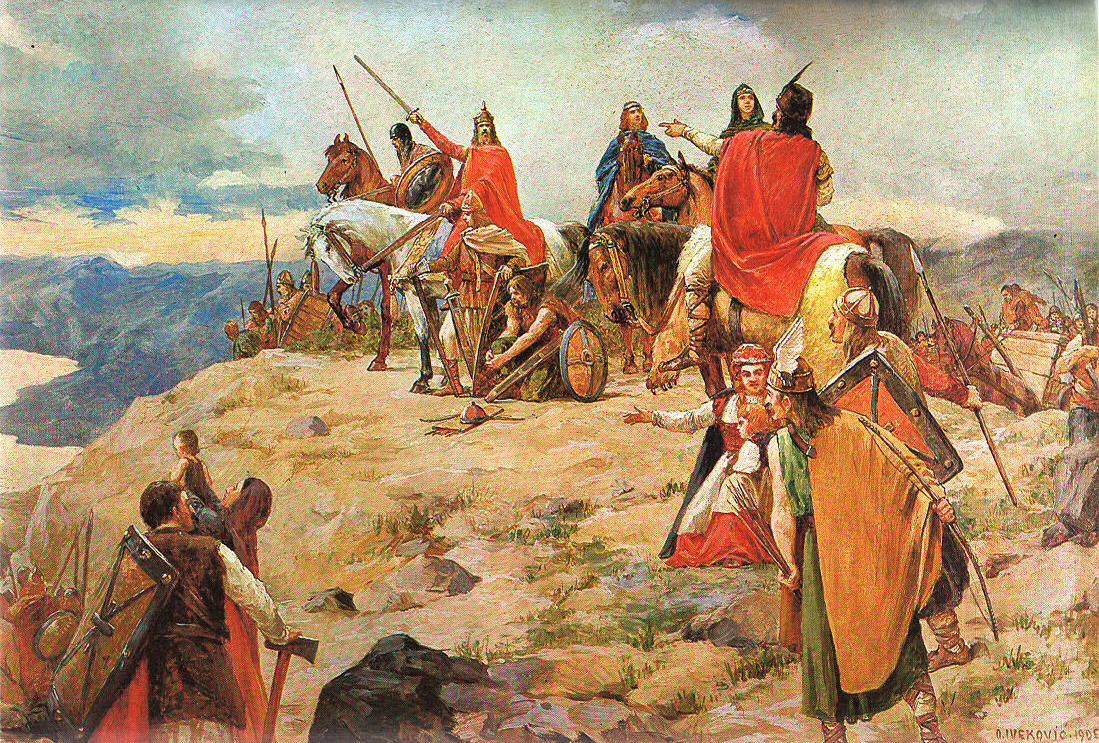
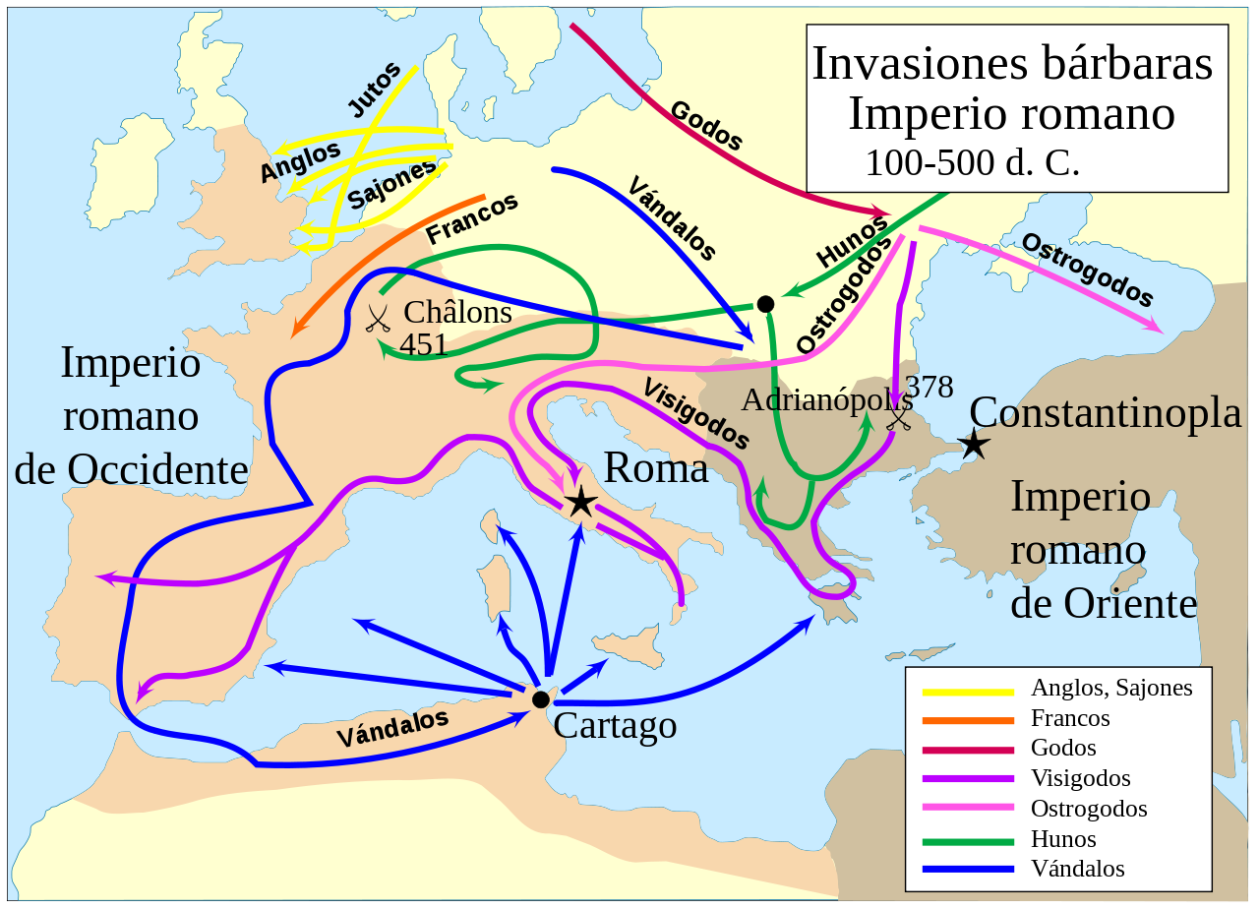
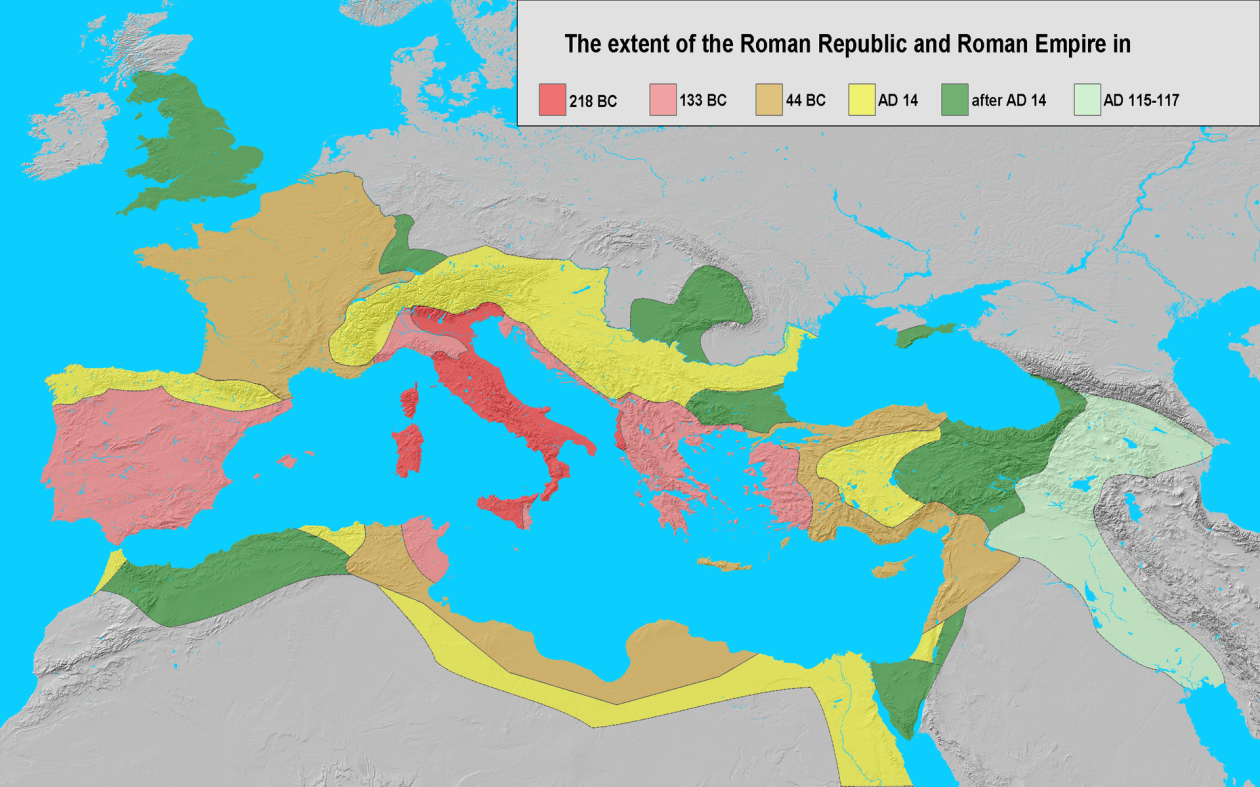
Los pueblos germanos o germánicos son un histórico grupo etnolingüístico de pueblos originarios del norte de Europa que se identifican por el uso de las lenguas germánicas (un subgrupo de la familia lingüística indoeuropea que se diversificaron a partir de una lengua original —reconstruible como idioma protogermánico— en el transcurso de la Edad de Hierro). En términos historiográficos son tanto un grupo de entre los pueblos prerromanos (en las zonas germanas al oeste del Rin —provincias de Germania Superior e Inferior— en que se estableció una fuerte presencia del Imperio romano y fueron romanizadas) como un grupo de pueblos bárbaros (exteriores al limes del Imperio), situados al este del Rin y al norte del Danubio (Germania Magna); precisamente el que protagonizó las denominadas invasiones germánicas que provocaron la caída del Imperio romano de Occidente al instalarse en amplias zonas de éste: suevos, vándalos, godos (visigodos y ostrogodos), francos, burgundios, turingios, alamanes, anglos, sajones, jutos, hérulos, rugios, lombardos, etc. Los vikingos protagonizaron posteriormente una nueva oleada expansiva desde Escandinavia (la zona originaria de todo este grupo de pueblos), que afectó a las costas atlánticas (normandos) y a las estepas rusas y Bizancio (varegos).
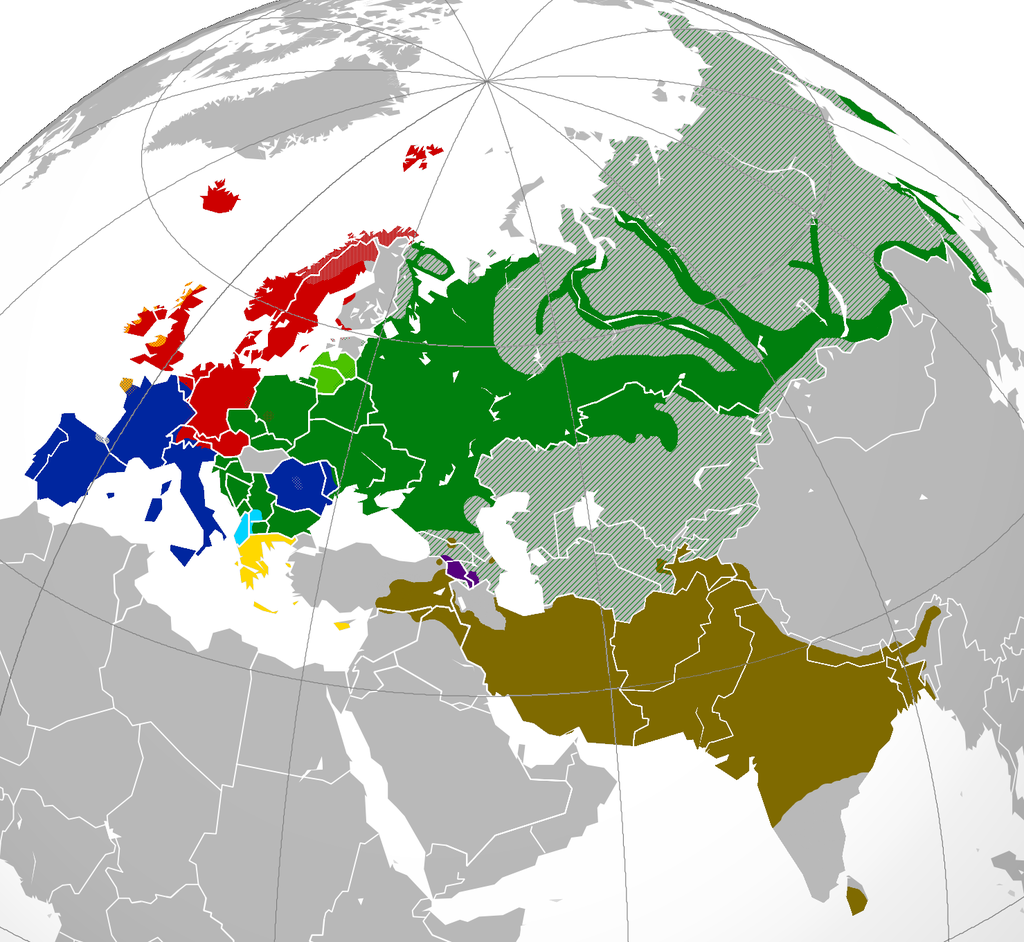
Algunos pueblos germánicos se fusionaron con la población romana dominante demográficamente en las zonas que ocuparon de Europa suroccidental (galo-romanos, hispano-romanos, italo-romanos); mientras que otros se convirtieron en la base etnográfica de las actuales poblaciones de Europa central y noroccidental (escandinavos o nórdicos -la mayor parte de los países nórdicos: daneses, suecos, noruegos, islandeses, y los isleños de las Islas Faroe, con excepción de bálticos, fineses y lapones-, alemanes -en el sentido del ámbito lingüístico alemán, que incluye a los austriacos, la mitad de los suizos y otros grupos de habla alemana de Europa central y oriental desde Francia hasta el Cáucaso-, las poblaciones de habla neerlandesa -noroeste de Alemania, Países Bajos y norte de Bélgica- y anglosajona). En Europa oriental los pueblos germánicos se vieron desplazados por otros (especialmente los pueblos eslavos y los magiares), para pasar posteriormente a protagonizar una nueva fase expansiva.
Las migraciones de los pueblos germánicos se extendieron por toda Europa durante la Antigüedad Tardía (Völkerwanderung) y la Edad Media (Ostsiedlung). Estos términos historiográficos se concibieron y utilizaron de forma no neutral, sino como justificación del expansionismo alemán hacia el este en la Edad contemporánea (Drang nach osten).
También en el ámbito religioso se produjo una fusión de los elementos germánicos y romanos: algunos ya habían sido cristianizados bajo credo arriano en Oriente en el siglo IV, otros continuaban con las religiones nórdicas tradicionales. La conversión al catolicismo de suevos visigodos y francos en el siglo VI fue clave para su éxito de la formación de sus respectivos reinos germánicos. Hacia el siglo XI todos los pueblos germánicos, incluidos los escandinavos, estaban incluidos en el ámbito de la cristiandad latina.
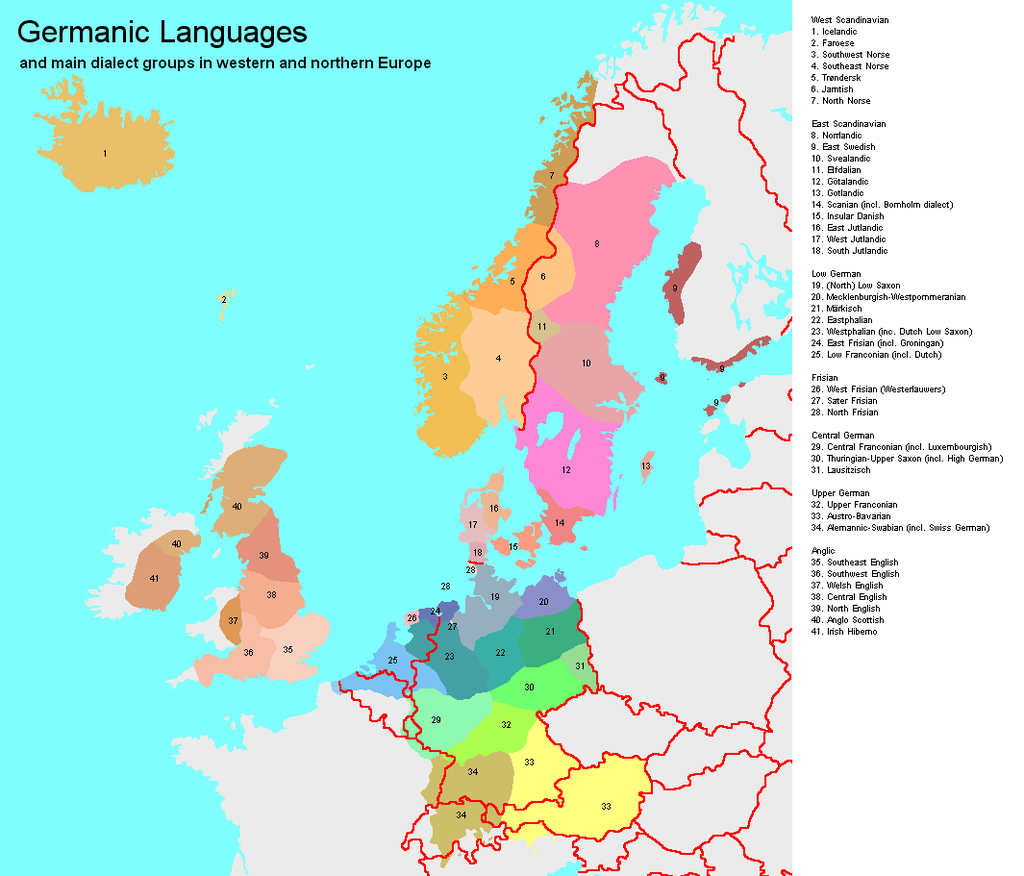
Las lenguas germánicas se convirtieron en dominantes a lo largo de las fronteras romanas (Austria, Alemania, Países Bajos, Bélgica e Inglaterra), pero en el resto de las provincias romanas occidentales, los inmigrantes germánicos adoptaron los dialectos latinos que se estaban transformando en lenguas romances. Actualmente las lenguas germánicas se hablan a través de gran parte del mundo, representadas principalmente por el inglés, alemán, neerlandés y las lenguas escandinavas.
==============……………………………=======================
Germanic peoples
The Teutons or Germanic peoples are a historical group ethnolinguistic peoples originating in Northern Europe which are identified by the use of the Germanic languages (a subgroup of the Indo-European language family that diversified from the original language as-reconstructable Proto language – during the Iron Age ). In historiographical terms are both a group from the Roman peoples (in Germanic areas west of the Rhine -provinces of Germania Superior and Inferior – that a strong presence of the established Roman Empire and were romanized ) as a group of barbarians ( Outside the limes of the empire), located east of the Rhine and north of the Danube ( Magna Germania ); precisely which starred called Germanic invasions that caused the fall of the Western Roman Empire to settle in large areas of éste: suevos , vándalos , godos ( visigodos y ostrogodos ), francos , burgundios , turingios , alamanes , anglos , sajones , jutos , hérulos , rugios , lombardos , etc. The Vikings then staged a new expansive wave from Scandinavia (the original area of this whole group of people), which hit the Atlantic coast ( Norman ) and the Russian steppes and Byzantium ( Varangians ).
Some Germanic peoples merged with the Roman population demographically dominant in areas occupied in southwestern Europe ( Gallo -Roman, Hispano -Romans, Italo -Romans); while others became ethnographic basis of current populations of Central Europe and northwestern ( Scandinavian or Nordic -most of the Nordic countries : Danish , Swedish , Norwegian , Icelandic , and the islanders of the Faroe Islands , except Baltic , Finns and Lapps – Germans in the sense of the German language area, which includes the Austrian half of the Swiss and other groups of German-speaking Central and Eastern Europe from France to the Caucasus – speaking populations Dutch -northwest Germany, the Netherlands and northern Belgium, and Anglo-Saxon ). In Eastern Europe the Germanic peoples were displaced by others (especially Slavs and Magyars ), before moving on to star in a new phase of expansion.
Migration of Germanic peoples spread throughout Europe during the Late Antiquity ( Völkerwanderung ) and the Middle Ages ( Ostsiedlung ). These historiographical terms were designed and used non-neutral, but as justification for German expansionism eastward into the Contemporary Age ( Drang nach osten ).
Also in the religious sphere there was a fusion of Germanic and Roman elements: some had already been Christianized by low credo Arian in the East in the fourth century, others continued with traditional Nordic religions. The conversion to Catholicism of Swabians Visigoths and Franks in the sixth century was key to success of the formation of their Germanic kingdoms . By the eleventh century all Germanic peoples, including Scandinavia, were included in the field of Latin Christendom .
Germanic languages became dominant along the Roman borders ( Austria , Germany , Netherlands , Belgium and England ), but the rest of the Roman provinces Western, Germanic immigrants adopted Latin dialects were becoming languages romances . Currently the Germanic languages are spoken through much of the world, mainly represented by the English , German , Dutch and the Scandinavian languages .