Reino de Northumbria.Historia.Religión.Edad Media
Reino de Northumbria
Northumbria (en sajón antiguo: Norþanhymbra; en nórdico antiguo: Norðimbraland, nombre que refleja su ubicación al norte del río Humber) fue uno de los reinos menores de los anglos, mencionado en el siglo XII por Enrique de Huntingdon como parte de la Heptarquía Anglosajona-juta, los dominios establecidos por los pueblos germánicos que comenzaron a invadir Gran Bretaña a finales del Siglo V, cuando ya hacía casi 70 años que había sido abandonada por las legiones romanas.
Fundada por anglos bajo el mando de Etelfrido (Ethelfrith) en lo que hoy es el noreste inglés en el año 593 a partir de la unión de otros dos reinos menores, Bernicia y Deira, floreció en el Siglo VII, llegando a extenderse por las Tierras Altas escocesas y Gales, desde el Humber hasta el Forth. Tuvo su capital en Whitby, sede del célebre sínodo homónimo que decidió en favor del rito cristiano romano frente al irlandés para ser implantado en tierras británicas.
El territorio northumbrio fue ocupado por los daneses en el siglo IX y se integró al reino de Inglaterra en 829, de la mano de las conquistas de Egberto de Wessex.
El condado que se formó después, estaba limitado al sur por el río Tees y al norte por el río Tweed (lo que hoy en día es similar a la región moderna del Noreste de Inglaterra) y fue reconocido como parte de Inglaterra por el Tratado de York de 1237 entre Inglaterra y Escocia. Berwick-upon-Tweed, que se sitúa al norte del Tweed, fue definido como súbdito de las leyes de Inglaterra por el Acta de Gales y Berwick de 1746. El territorio que una vez fue parte de Northumbria durante su apogeo es administrado hoy en día por regiones diferentes como Noreste de Inglaterra (Bernicia), Yorkshire y Humber (Deira), Noroeste de Inglaterra (Cumbria), los Scottish Borders, West Lothian, Edimburgo, Midlothian y East Lothian.
Actualmente, Northumbria es la región Noreste de Inglaterra. El nombre se usa en los títulos de la Policía de Northumbria (la cual administra Northumberland y Tyne y Wear) y la Universidad de Northumbria (ubicada en Newcastle), y también ha sido adoptado por la Junta de Turismo de Inglaterra para referirse al Noreste de Inglaterra.
Historia
Northumbria originalmente estaba compuesta por la unión de dos reinos dependientes, Bernicia y Deira. Bernicia cubría el territorio norte del río Tees, mientras Deira correspondía a lo que hoy en día es aproximadamente Yorkshire. Bernicia y Deira fueron unidos por primera vez por Eteelfrido, un rey de Bernicia que conquistó Deira alrededor del año 604. Fue derrotado y murió en 616 en una batalla cerca del río Idle a manos de Raedwald, rey de Anglia Oriental, quien instaló a Edwin, el hijo de Aella, un antiguo rey de Deira, como el nuevo rey de Northumbria.
Edwin de Northumbria, que aceptó el cristianismo en 627, pronto se convirtió en el rey más poderoso de Inglaterra: fue reconocido como Bretwalda y conquistó la Isla de Man y el Reino de Gwynedd, en el norte de Gales. Sin embargo, fue derrotado por una alianza entre el rey exiliado de Gwynedd, Cadwallon ap Cadfan, y Penda, rey de Mercia, en la batalla de Hatfield Chase en 633.
Religión
En el año 664 un gran sínodo tuvo lugar en Whitby para discutir la controversia de la fecha de las fiestas de Pascua. Muchos conflictos se habían manifestado entre las prácticas de la Iglesia Celta en Northumbria y las creencias de la Iglesia Católica. Finalmente, Northumbria fue persuadida de retomar las creencias de la fe católica, y el obispo celta, Colman de Lindisfarne, volvió a Iona.

Libro de Kells, Folio 292r, introducción al Evangelio de Juan («In principio erat verbum»).
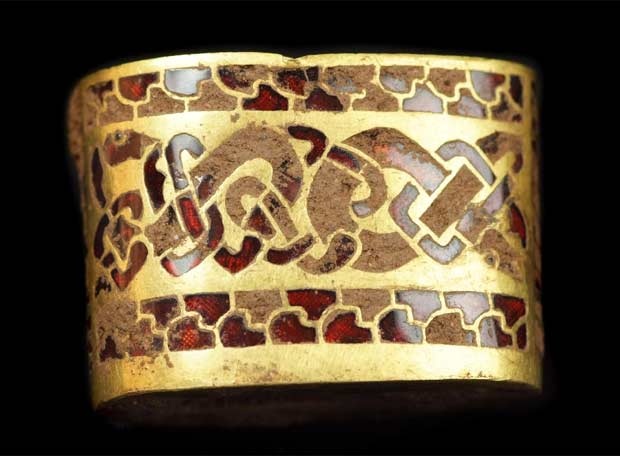
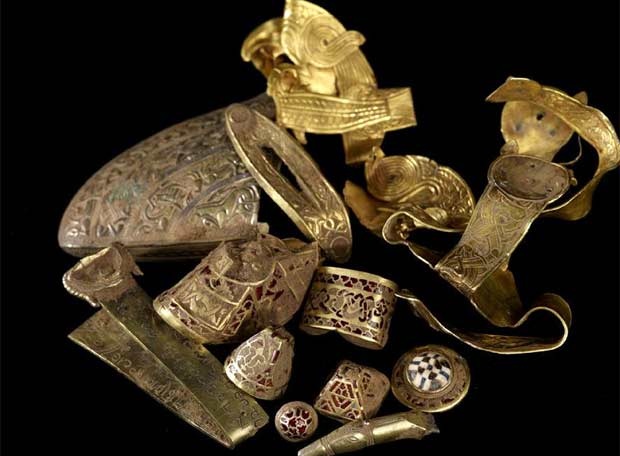
El reino fue afamado como centro religioso y artístico. Inicialmente Northumbria fue cristianizada por monjes de la Iglesia Celta, y esto llevó al florecimiento de la vida monástica, con un estilo de arte religioso único que combinaba estilos anglosajones y celtas. Después del Sínodo de Whitby en 664 la Iglesia Celta y la Romana se unieron. Sin embargo, el estilo único de arte religioso fue preservado y promovido, cuyo ejemplo más famoso son los Evangelios de Lindisfarne.
Edad Media
La región tuvo una larga historia de disturbios y revueltas en contra del poder establecido, como se vio en la Peregrinación de Gracia y el Levantamiento del Norte en los tiempos de la Casa de Tudor. La mayor razón fue la fuerza del catolicismo en el área después de la Reforma religiosa que instauró el anglicanismo. Ello llevó a un fervoroso sentimiento jacobita tras la Restauración Inglesa. La región cobró la fama de ser un condado salvaje, donde fugitivos y separatistas se escondían de la ley, ya que era mayoritariamente rural y poco poblada. Sin embargo, después de la unión de Escocia e Inglaterra, en 1603, la paz volvió a ser instaurada.
Nº 10. Palabra: Río HUMBER.
Traducción: River HUMBER.
Kingdom of Northumbria
Northumbria (in Old Saxon : Norþanhymbra, in Old Norse : Norðimbraland, a name that reflects its location north of the river Humber ) was one of the smaller kingdoms of Anglo mentioned in the twelfth century by Henry of Huntingdon as part of the Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy -juta, domains established by the Germanic peoples began to invade Britain at the end of V century , when it was almost 70 years that had been abandoned by the legions Roman .
Founded by Anglo under the command of Etelfrido (Ethelfrith) in what is now northeastern English in the year 593 from the union of two smaller kingdoms, Bernicia and Deira , flourished in the seventh century , reaching extend the Lands High Scottish and Wales , from the Humber to the Forth . It had its capital in Whitby , home of the famous namesake synod decided in favor of the Christian Roman rite against the Irish to be implanted on British soil.
The Northumbrian territory was occupied by the Danes in the ninth century and joined the Kingdom of England in 829 , at the hands of the conquests of Egbert of Wessex .
The county was formed later, was bounded on the south by the River Tees and north of the River Tweed (which today is similar to the modern region of North East England) and was recognized as part of England by the Treaty of York in 1237 between England and Scotland. Berwick-upon-Tweed , which lies to the north of the Tweed, was defined as subject to the laws of England by the Wales and Berwick Act of 1746 . The territory that was once part of Northumbria at its peak is managed today by different regions like North East England ( Bernicia ), Yorkshire and Humber ( Deira ), North West ( Cumbria ), the Scottish Borders , West Lothian , Edinburgh , Midlothian and East Lothian .
Currently, Northumbria is the Northeast of England. The name is used in the titles of Northumbria Police (which administers Northumberland and Tyne and Wear ) and the University of Northumbria (based in Newcastle ), and has also been adopted by the Board of Tourism England to refer to Northeast England.
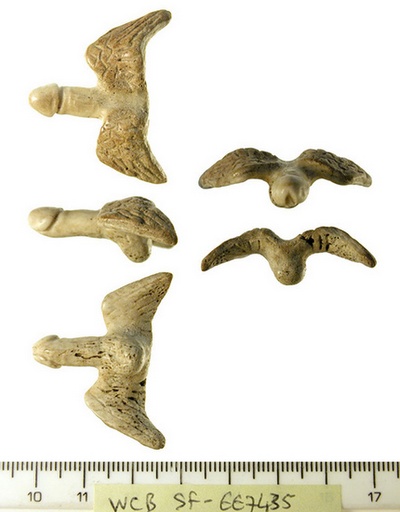
**************************************************************************************************»PENES CON ALAS ( UTILIZADOS POR LOS ROMANOS CONTRA EL MAL DE OJO )»
History
Northumbria was originally composed by the union of two dependent kingdoms, Bernicia and Deira . Bernicia covered the territory north of the River Tees , while Deira corresponded to what today is about Yorkshire . Bernicia and Deira were united first by Æthelfrith a king of Bernicia who conquered Deira around the year 604 . He was defeated and died in 616 in a battle near the river Idle hands of Raedwald king of East Anglia , who installed Edwin , the son of Aella , a former king of Deira, as the new king of Northumbria.
Edwin of Northumbria, who accepted Christianity in 627 , soon became the most powerful king in England: he was recognized as Bretwalda and conquered the Isle of Man and the Kingdom of Gwynedd , in North Wales . However, he was defeated by an alliance of the exiled king of Gwynedd , Cadwallon ap Cadfan , and Penda , king of Mercia , at the Battle of Hatfield Chase in 633 .
«BANDERA» «FLAG»
«FLAG»
Religion
In the year 664 a great synod was held at Whitby to discuss the controversy over the date of the festival of Easter . Many conflicts had emerged between the practices of the Celtic Church in Northumbria and the beliefs of the Catholic Church. Eventually, Northumbria was persuaded to return to the beliefs of the faith Catholic , and the Celtic Bishop Colman of Lindisfarne returned to Iona.

Book of Kells, Folio 292r, introduction to the Gospel of John («In principio erat Verbum»).
The kingdom was famous as a religious and cultural center. Initially Northumbria was Christianized by monks of the Celtic Church, and this led to the flowering of monastic life, with a unique style of religious art styles that combined Anglo-Saxon and Celtic . After the Synod of Whitby in 664 the Celtic Church and the Roman joined. However, the unique style of religious art was preserved and promoted, the most famous example is the Lindisfarne Gospels .
Middle Ages
The region has a long history of riots and revolts against the established power, as seen in the Pilgrimage of Grace and the Northern Rising in the time of the House of Tudor . The biggest reason was the strength of Catholicism in the area after the Reformation which established Anglicanism . This led to a fervent feeling Jacobite after the English Restoration . The region gained a reputation as a wild county, where separatists were hiding fugitives from the law, as it was largely rural and sparsely populated. However, after the union of Scotland and England, in 1603, peace was again instituted.
Fuente que utilizo: http://es.wikipedia.org