| Leonardo da Vinci | |
|---|---|
 Leonardo da Vinci, Autorretrato hecho entre 1512 y1515.1 Nota 1 |
|
| Nombre completo | Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci |
| Nacimiento | 15 de abril de 1452 |
| Fallecimiento | 2 de mayo de 1519 (67 años) |
| Nacionalidad | |
| Ocupación | Arquitecto, escultor, ingeniero,inventor y pintor |
| Movimiento | Renacimiento |
| Firma | |
Leonardo da Vinci (Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci ![]() escuchar) fue un pintorflorentino. Notable polímata del Renacimiento italiano (a la vez anatomista, arquitecto,artista, botánico, científico, escritor, escultor,filósofo, ingeniero, inventor, músico,poeta y urbanista) nació en Vinci el 15 de abril de 14522 y falleció en Amboise el 2 de mayo de 1519, a los 67 años, acompañado de su fiel Francesco Melzi, a quien legó sus proyectos, diseños y pinturas.2 Tras pasar su infancia en su ciudad natal, Leonardo estudió con el célebre pintor florentino Andrea de Verrocchio. Sus primeros trabajos de importancia fueron creados en Milán al servicio del duque Ludovico Sforza. Trabajó a continuación en Roma, Bolonia y Venecia, y pasó los últimos años de su vida en Francia, por invitación del rey Francisco I.
escuchar) fue un pintorflorentino. Notable polímata del Renacimiento italiano (a la vez anatomista, arquitecto,artista, botánico, científico, escritor, escultor,filósofo, ingeniero, inventor, músico,poeta y urbanista) nació en Vinci el 15 de abril de 14522 y falleció en Amboise el 2 de mayo de 1519, a los 67 años, acompañado de su fiel Francesco Melzi, a quien legó sus proyectos, diseños y pinturas.2 Tras pasar su infancia en su ciudad natal, Leonardo estudió con el célebre pintor florentino Andrea de Verrocchio. Sus primeros trabajos de importancia fueron creados en Milán al servicio del duque Ludovico Sforza. Trabajó a continuación en Roma, Bolonia y Venecia, y pasó los últimos años de su vida en Francia, por invitación del rey Francisco I.
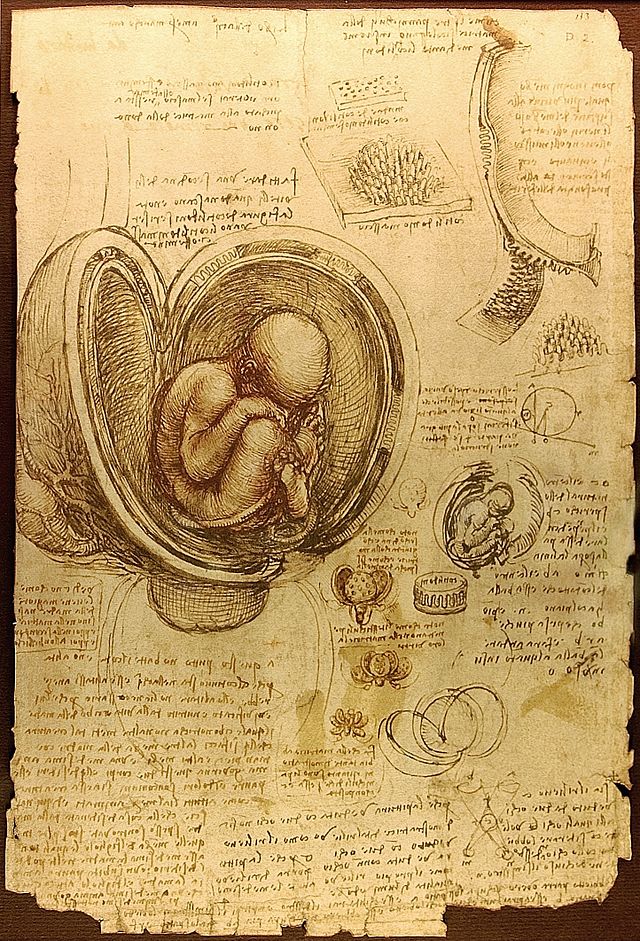
Frecuentemente descrito como un arquetipo y símbolo del hombre del Renacimiento,genio universal, además de filósofo humanista cuya curiosidad infinita solo puede ser equiparable a su capacidad inventiva,3Leonardo da Vinci es considerado como uno de los más grandes pintores de todos los tiempos y, probablemente, es la persona con el mayor número de talentos en múltiples disciplinas que jamás ha existido.4 Como ingeniero e inventor, Leonardo desarrolló ideas muy adelantadas a su tiempo, tales como el helicóptero, el carro de combate, el submarino y el automóvil. Muy pocos de sus proyectos llegaron a construirse (entre ellos la máquina para medir el límite elástico de un cable),Nota 2 puesto que la mayoría no eran realizables durante esa época.Nota 3 Como científico, Leonardo da Vinci hizo progresar mucho el conocimiento en las áreas deanatomía, la ingeniería civil, la óptica y la hidrodinámica.
Su asociación histórica más famosa es la pintura, siendo dos de sus obras más célebres,La Gioconda y La Última Cena, copiadas y parodiadas en varias ocasiones, al igual que su dibujo del Hombre de Vitruvio, que llegaría a ser retomado en numerosos trabajos derivados. No obstante, únicamente se conocen unas veinte de sus obras, debido principalmente a sus constantes (y a veces desastrosos) experimentos con nuevas técnicas y a su inconstancia crónica.Nota 4 Este reducido número de creaciones, junto con sus cuadernos que contienen dibujos, diagramas científicos y reflexiones sobre la naturaleza de la pintura, constituyen un legado para las sucesivas generaciones de artistas, llegando a ser igualado únicamente por Miguel Ángel.
_____________________________…………………………===========================
Leonardo da Vinci
| Leonardo da Vinci | |
|---|---|

Portrait of Leonardo by Melzi
|
|
| Born | Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci April 15, 1452 Vinci, Republic of Florence(present-day Italy) |
| Died | May 2, 1519 (aged 67) Amboise, Kingdom of France |
| Known for | Diverse fields of the arts and sciences |
| Notable work(s) | Mona Lisa The Last Supper The Vitruvian Man Lady with an Ermine |
| Style | High Renaissance |
| Signature | |
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (Italian: [leoˈnardo da vˈvintʃi] (![]() ); 15 April 1452 – 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath, painter, sculptor, architect, musician, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist,cartographer, botanist, and writer. He is widely considered to be one of the greatest painters of all time and perhaps the most diversely talented person ever to have lived.[1] His genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance humanist ideal. Leonardo has often been described as the archetype of the Renaissance Man, a man of “unquenchable curiosity” and “feverishly inventive imagination”.[2] According to art historian Helen Gardner, the scope and depth of his interests were without precedent and “his mind and personality seem to us superhuman, the man himself mysterious and remote”.[2] Marco Rosci states that while there is much speculation about Leonardo, his vision of the world is essentially logical rather than mysterious, and that the empirical methods he employed were unusual for his time.[3]
); 15 April 1452 – 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath, painter, sculptor, architect, musician, mathematician, engineer, inventor, anatomist, geologist,cartographer, botanist, and writer. He is widely considered to be one of the greatest painters of all time and perhaps the most diversely talented person ever to have lived.[1] His genius, perhaps more than that of any other figure, epitomized the Renaissance humanist ideal. Leonardo has often been described as the archetype of the Renaissance Man, a man of “unquenchable curiosity” and “feverishly inventive imagination”.[2] According to art historian Helen Gardner, the scope and depth of his interests were without precedent and “his mind and personality seem to us superhuman, the man himself mysterious and remote”.[2] Marco Rosci states that while there is much speculation about Leonardo, his vision of the world is essentially logical rather than mysterious, and that the empirical methods he employed were unusual for his time.[3]
Born out of wedlock to a notary, Piero da Vinci, and a peasant woman, Caterina, in Vinciin the region of Florence, Leonardo was educated in the studio of the renowned Florentine painter Verrocchio. Much of his earlier working life was spent in the service of Ludovico il Moro in Milan. He later worked in Rome, Bologna and Venice, and he spent his last years in France at the home awarded him by Francis I.
Leonardo was, and is, renowned primarily as a painter. Among his works, the Mona Lisais the most famous and most parodied portrait[4] and The Last Supper the most reproduced religious painting of all time, with their fame approached only byMichelangelo‘s The Creation of Adam.[2] Leonardo’s drawing of the Vitruvian Man is also regarded as a cultural icon,[5] being reproduced on items as varied as the euro coin, textbooks, and T-shirts. Perhaps fifteen of his paintings have survived, the small number because of his constant, and frequently disastrous, experimentation with new techniques, and his chronic procrastination.[nb 1] Nevertheless, these few works, together with his notebooks, which contain drawings, scientific diagrams, and his thoughts on the nature of painting, compose a contribution to later generations of artists rivalled only by that of his contemporary, Michelangelo.
Leonardo is revered for his technological ingenuity. He conceptualised flying machines, an armoured vehicle, concentrated solar power, an adding machine,[6] and the double hull, also outlining a rudimentary theory ofplate tectonics. Relatively few of his designs were constructed or were even feasible during his lifetime,[nb 2] but some of his smaller inventions, such as an automated bobbin winder and a machine for testing the tensile strength of wire, entered the world of manufacturing unheralded.[nb 3] He made important discoveries in anatomy, civil engineering, optics, and hydrodynamics, but he did not publish his findings and they had no direct influence on later science.[7]
Fuente: