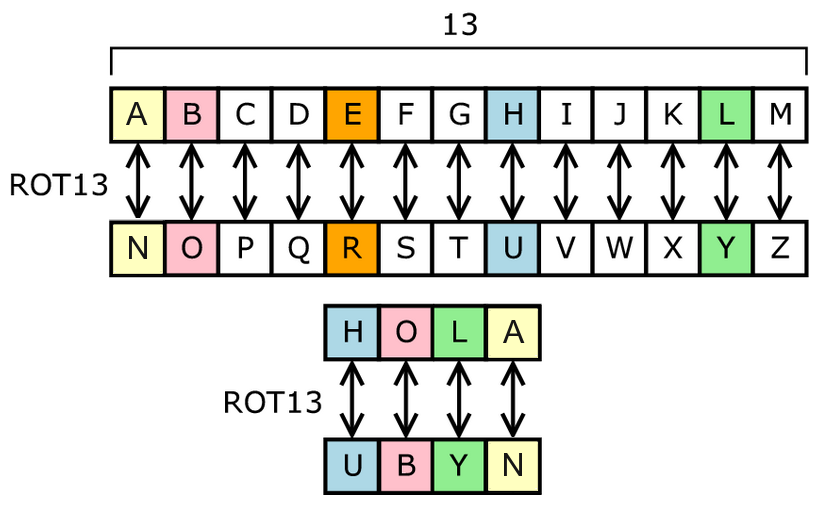
ROT13 («rotar 13 posiciones», a veces con un guion: ROT-13) es un sencillocifrado César utilizado para ocultar un texto sustituyendo cada letra por la letra que está trece posiciones por delante en el alfabeto. Ase convierte en N, B se convierte en Oy así hasta la M, que se convierte en Z. Luego la secuencia se invierte: N se convierte enA, O se convierte en B y así hasta la Z, que se convierte en M. Este algoritmo se utiliza en foros de Internet como medio para ocultar de miradas casuales el final de unchiste, la solución a un acertijo, un spoiler de una película o una historia, o algúntexto ofensivo. ROT13 se ha descrito como el «equivalente en Usenet de una revista que imprime bocabajo la respuesta a un pasatiempo».1
El nombre «ROT13» se originó en Usenet a principios de los años 1980, y el método se ha convertido en un estándar de facto. Al igual que el cifrado de César (un método de cifrado con miles de años), el ROT13 no proporciona seguridad criptográfica real y no se usa para tales fines; de hecho, a menudo se emplea como ejemplo canónico de cifrado débil. Otra característica de este cifrado es que es simétrico; esto es, para deshacer el ROT13, se aplica el mismo algoritmo, de manera que para cifrar y descrifrar se puede utilizar el mismo código.
Descripción
Aplicar el ROT13 a un texto se reduce a examinar sus caracteres alfabéticos y sustituirlos por la letra que está 13 posiciones por delante en el alfabeto, volviendo al principio si es necesario y conservando las mayúsculas y minúsculas: a se convierte en n, B se convierte en O, y así hasta la Z, que se convierte en M. Solo quedan afectadas las letras que aparecen en el alfabeto latino; los números, símbolos, espacios y otros caracteres se dejan igual. Como hay 26 letras en el alfabeto latino y 26 = 2 × 13, la función ROT13 es su propiainversa:
 para cualquier texto x.
para cualquier texto x.
En otras palabras, dos aplicaciones sucesivas de ROT13 recuperan el texto original (en matemáticas, esto a veces se llama involución; en criptografía, un cifrado recíproco).
La transformación se puede hacer utilizando una tabla de búsqueda como la siguiente:
| ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz |
| NOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklm |
Por ejemplo, en este chiste, la respuesta se ha ocultado usando ROT13:
¿Cómo se puede distinguir a un extrovertido de un introvertido en la NSA? Ra ybf nfprafberf, ry rkgebiregvqb zven ybf mncngbf qr ybf BGEBF gvcbf.
Transformando todo el texto mediante el ROT13, se revela la respuesta al chiste:
¿Pbzb fr chrqr qvfgvathve n ha rkgebiregvqb qr ha vagebiregvqb ra yn AFN? En los ascensores, el extrovertido mira los zapatos de los OTROS tipos.
Una segunda aplicación del ROT13 recuperaría el original.
____________________________………………………=================================
ROT13
ROT13 (“rotate by 13 places“, sometimes hyphenated ROT-13) is a simple lettersubstitution cipher that replaces a letter with the letter 13 letters after it in the alphabet. ROT13 is an example of the Caesar cipher, developed in ancient Rome.
In the basic Latin alphabet, ROT13 is its own inverse; that is, to undo ROT13, the same algorithm is applied, so the same action can be used for encoding and decoding. The algorithm provides virtually nocryptographic security, and is often cited as a canonical example of weak encryption.
ROT13 is used in online forums as a means of hiding spoilers, punchlines, puzzle solutions, and offensive materials from the casual glance. ROT13 has been described as the “Usenet equivalent of a magazineprinting the answer to a quiz upside down“.[1] ROT13 has inspired a variety of letter and word games on-line, and is frequently mentioned in newsgroup conversations.
Description
Applying ROT13 to a piece of text merely requires examining its alphabetic characters and replacing each one by the letter 13 places further along in thealphabet, wrapping back to the beginning if necessary.[2] A becomes N, B becomes O, and so on up to M, which becomes Z, then the sequence continues at the beginning of the alphabet: N becomes A, O becomes B, and so on to Z, which becomes M. Only those letters which occur in the English alphabet are affected; numbers, symbols, whitespace, and all other characters are left unchanged. Because there are 26 letters in the English alphabet and 26 = 2 × 13, the ROT13 function is its own inverse:[2]
 for any basic Latin-alphabet text x.
for any basic Latin-alphabet text x.
In other words, two successive applications of ROT13 restore the original text (inmathematics, this is sometimes called an involution; in cryptography, a reciprocal cipher).
The transformation can be done using a lookup table, such as the following:
| ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz |
| NOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKLMnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklm |
For example, in the following joke, the punchline has been obscured by ROT13:
Why did the chicken cross the road? Gb trg gb gur bgure fvqr!
Transforming the entire text via ROT13 form, the answer to the joke is revealed:
Jul qvq gur puvpxra pebff gur ebnq? To get to the other side!
A second application of ROT13 would restore the original.